Kidney Risks in Vaccination
Bombshell Global Study Links mRNA Vaccines to Serious Increased Kidney Injury Outcomes
A recent global study published in Scientific Reports analyzed over 120.7 million adverse event reports from the World Health Organization’s VigiBase, spanning 1967 to 2022, to investigate vaccine-associated kidney injuries. Led by Dr. Hyeon Seok Hwang, the research found a significant increase in kidney-related adverse events following the rollout of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines starting in 2020. Specifically, the study identified elevated reporting odds ratios (ROR) for three kidney conditions linked to mRNA vaccines: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) with an ROR of 2.38 (2.4 times higher than expected), Glomerulonephritis (GN) with an ROR of 13.41 (13.4 times higher), and Tubulointerstitial Nephritis (TIN) with an ROR of 2.43 (2.4 times higher).
These findings indicate a disproportionate reporting of kidney issues compared to other vaccines and drugs in the database.
The study noted that AKI reports often coincided with serious neurological and cardiovascular events, suggesting a multi-system impact. For GN, the median onset was about 7.2 days post-vaccination, with a 25% rate of serious outcomes, while TIN had a median onset of 2 days and a 23% serious outcome rate. Although other vaccines, like hepatitis B and HPV, also showed kidney-related signals, the mRNA vaccines stood out for their scale and strength of association.
Despite these findings, the absolute risk remains low, given the billions vaccinated globally, and the study emphasizes the overwhelming benefits of COVID-19 vaccination while calling for further research into high-risk populations and vaccine safety monitoring.
This aligns with independent analyses, such as John Beaudoin Sr.'s U.S. data review, which linked over 210,000 excess AKI deaths since 2021 to mRNA vaccines and hospital protocols. The study raises critical questions about underreported renal adverse events and the need for transparent, ongoing pharmacovigilance.
The article from TrialSite News, titled "Bombshell Global Study Links mRNA Vaccines to Serious Increased Kidney Injury Outcomes," discusses a significant pharmacovigilance study published in Scientific Reports. This research, led by Dr. Hyeon Seok Hwang from Kyung Hee University Medical Center in South Korea, analyzed a massive dataset of 120.7 million adverse event reports from the World Health Organization’s VigiBase, covering the period from 1967 to 2022. The study's primary focus was to evaluate the association between vaccines—particularly COVID-19 mRNA vaccines—and kidney-related adverse events (AEs), including Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), Glomerulonephritis (GN), and Tubulointerstitial Nephritis (TIN). Below is an expanded summary and analysis based on the article’s key points:
Key Findings of the Study Increased Reporting Post-2020: The study observed a gradual increase in kidney-related AEs over the decades, but a sharp and significant spike occurred after 2020, coinciding with the global rollout of COVID-19 vaccines. This temporal correlation suggests a potential link to the widespread administration of these vaccines, particularly mRNA-based ones like Pfizer-BioNTech’s BNT162b2 and Moderna’s mRNA-1273.
Disproportionate Signals for mRNA Vaccines: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): The reporting odds ratio (ROR) for AKI associated with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines was 2.38, meaning reports of AKI were 2.4 times higher than expected compared to the entire database of drugs and vaccines. AKI often presented alongside serious neurological (e.g., Guillain-Barré syndrome) and cardiovascular (e.g., arrhythmias) events, indicating a possible multi-system impact.
Glomerulonephritis (GN): GN showed the strongest signal, with an ROR of 13.41—indicating reports were 13.4 times higher than expected. The median onset was approximately 7.2 days post-vaccination, with 25% of cases classified as serious (e.g., requiring hospitalization or resulting in death/permanent disability). Tubulointerstitial Nephritis (TIN): TIN had an ROR of 2.43, with a median onset of just 2 days and a 23% rate of serious outcomes. This rapid onset suggests an acute inflammatory response potentially triggered by the vaccine. Comparison to Other Vaccines: While other vaccines, such as those for hepatitis B (ROR 11.35 for GN) and HPV, also showed elevated kidney injury signals, the mRNA vaccines were unique in both the scale and consistency of reported kidney AEs. The study highlighted that the disproportionate reporting for AKI and TIN was statistically significant only for COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, setting them apart from historical vaccine safety profiles.
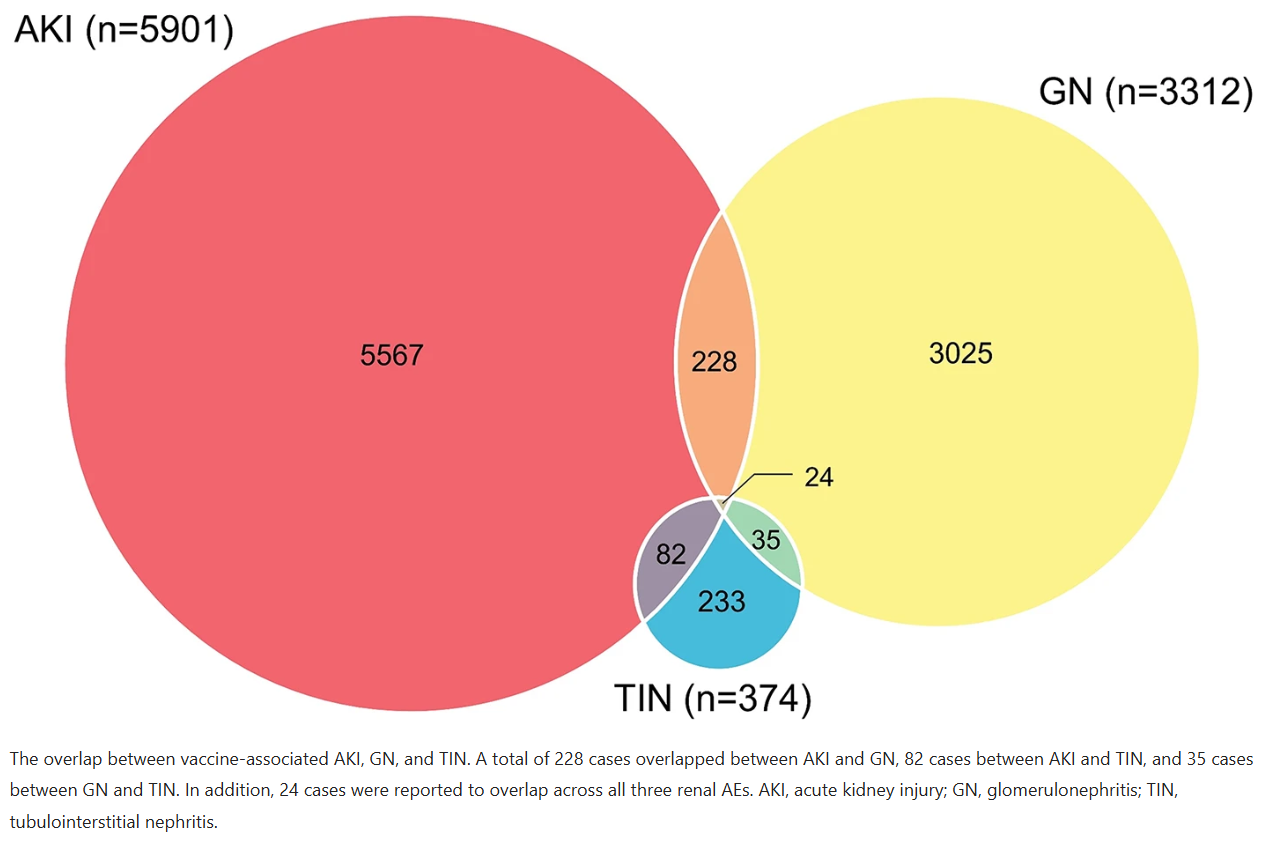
Global Distribution and Severity: The Americas and Europe reported the highest numbers of these kidney-related AEs, likely reflecting higher vaccination rates and robust pharmacovigilance systems. Many cases involved overlapping conditions (e.g., AKI and GN occurring together), and some patients experienced severe outcomes, including progression to chronic kidney disease or death.
Supporting Evidence: The article ties these findings to independent U.S.-based analyses by John Beaudoin Sr., who identified over 210,000 excess AKI deaths since 2021, potentially linked to mRNA vaccines and hospital protocols (e.g., use of nephrotoxic drugs like remdesivir). This suggests that the study’s results may reflect a broader, underreported phenomenon.
While the study does not establish causality, it speculates on mechanisms such as immune-mediated injury (e.g., molecular mimicry or excessive cytokine release) triggered by the mRNA vaccines’ spike protein production. These could lead to inflammation in kidney tissues, particularly in susceptible individuals. Risk vs. Benefit: Despite the alarming signals, the article notes that absolute risk remains low given the billions of doses administered globally. The study’s authors and the article emphasize that the overwhelming benefits of COVID-19 vaccination in reducing severe illness and mortality outweigh these rare risks for most populations. Implications and Critiques
Call for Further Research: The study urges deeper investigation into high-risk groups (e.g., elderly, those with pre-existing kidney conditions) and improved safety monitoring. It highlights a gap in current pharmacovigilance, as kidney AEs may be underreported or misattributed to other causes. Public Health Policy: The findings raise questions about informed consent and whether vaccine safety data adequately captured these risks during initial trials. The article suggests that governments and health agencies have been slow to acknowledge or support those affected by such adverse events. Limitations: As a pharmacovigilance study, it relies on spontaneous reporting, which can overestimate associations due to reporting bias (e.g., heightened awareness during the pandemic) and cannot confirm causation. The lack of a control group or detailed patient histories limits definitive conclusions.
The article frames this study as a "bombshell" due to its scale and implications, aligning it with growing scrutiny of mRNA vaccine safety. It contrasts the establishment narrative of vaccines as universally safe with emerging data suggesting rare but serious side effects. This tension underscores the need for transparent, ongoing evaluation of vaccine safety, especially as mRNA technology becomes a cornerstone of future therapeutics. In summary, the study provides compelling evidence of a statistical link between mRNA COVID-19 vaccines and increased kidney injury reports, particularly AKI, GN, and TIN. While not proving causation, it adds to a body of data challenging the blanket safety claims of these vaccines, urging a nuanced discussion of risks alongside undeniable benefits. Further clinical and mechanistic studies are critical to clarify these associations and guide future vaccination strategies.
Dig In trialsitenews.com Nature.com
